Polynomials
Class-9-Mathematics-1-Chapter-3-Maharashtra Board
Solutions- Practice Set and Problem Sets
Practice set 3.1
Question 1.1. State whether the given algebraic expressions are polynomials ? Justify.
(i) y + \(\frac{1}{y}\)
(ii) 2 − 5\(\sqrt{x}\)
(iii) x2 + 7x + 9
(iv) 2m−2 + 7m − 5
(v) 10
In an algebraic expression, if the powers of the variables are whole numbers then the algebraic expression is a polynomial.
(i) Not a polynomial.
y + \(\frac{1}{y}\) = y + y−1. Here, one of the powers of y is −1, which is not a whole number. So, y + \(\frac{1}{y}\) is not a polynomial.
(ii) Not a polynomial.
5\(\sqrt{x}\) = 5x1/2. Here, the power of x is \(\frac{1}{2}\) The power is not whole number.
(iii) Is a polynomial.
x2 + 7x + 9. Here, the powers of the variable x are 2, 1 and 0, which are whole numbers.
(iv) Not a polynomial.
2m−2 + 7m − 5. Here, one of the powers of m is −2, which is not a whole number
(v) Is a polynomial.
10 = 10x0. Here, the power of x is 0, which is a whole numbers. So, 10 is a polynomial (or constant polynomial).
Question 1.2. Write the coefficient of m3 in each of the given polynomial.
(i) m3
(ii) \(−\frac{3}{2}\) + m − \(\sqrt{3}\)m3
(iii) \(−\frac{2}{3}\)m3 − 5m2 + 7m − 1
The coefficients of m3 in the given polynomials are as follows :
(i) 1 (ii) −\(\sqrt{3}\) (iii) \(−\frac{2}{3}\).
Question 1.3. Write the polynomial in x using the given information.
(i) Monomial with degree 7
(ii) Binomial with degree 35
(iii) Trinomial with degree 8
A polynomial having only one term is called a monomial. Also, the highest power of the variable in a polynomial is called the degree of the polynomial.
(i) 4x7 is a monomial in x with degree 7.
(ii) 12x35 − x7 is a Binomial in x with degree 35.
(ii) 3x8 − 2x5 + 8 is a Trinomial in x with degree 8.
Question 1.4. Write the degree of the given polynomials.
(i) \(\sqrt{5}\)
(ii) x°
(iii) x2
(iv) \(\sqrt{2}\)m10 − 7
(v) 2p − \(\sqrt{7}\)
(vi) 7y − y3 + y5
(vii) xyz + xy − z
(viii) m3n7 − 3m5n + mn
The highest power of the variable in a polynomial of one variable is called the degree of the polynomial. Also, the highest sum of the powers of the variables in each term of the polynomial in more than one variable is the degree of the polynomial.
∴ the degree of the given polynomials is
(i) 0 …(∵ \(\sqrt{5}\) is a constant term);
(ii) 0
(iii) 2
(iv) 10
(v) 1 …(∵ p means p1);
(vi) 5
(vii) 3 ….(∵ xyz : 1 + 1 + 1 = 3)
(viii) 10 ….(∵ m3n7 : 3 + 7 = 10).
Question 1.5. Classify the following polynomials as linear, quadratic and cubic polynomial.
(i) 2x2 + 3x + 1
The degree of the polynomial 2x2 + 3x + 1 is 2.
∴ the polynomial 2x2 + 3x + 1 is a quadratic polynomial.
(ii) 5p
The degree of the polynomial 5p is 1.
∴ the polynomial 5p is a linear polynomial.
(iii) \(\sqrt{2}\)y – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
The degree of the polynomial \(\sqrt{2}\)y – \(\frac{1}{2}\) is 1.
So, the polynomial \(\sqrt{2}\)y – \(\frac{1}{2}\) is a linear polynomial.
(iv) m3 + 7m2 + \(\frac{5}{2}\) m − 7
The degree of the polynomial m3 + 7m2 + \(\frac{5}{2}\)m − 7 is 3.
So, the polynomial m3 + 7m2 + \(\frac{5}{2}\)m − 7 is a cubic polynomial.
(v) a2
The degree of the polynomial a2 is 2.
∴ the polynomial a2 is a quadratic polynomial.
(vi) 3r3
The degree of the polynomial 3r3 is 3.
∴ the polynomial 3r3 is a cubic polynomial.
Question 1.6. Write the following polynomials in standard form.
(i) m3 + 3 + 5m
A polynomial written in either descending or ascending powers of its variable is called the standard form of the polynomial.
The given polynomial is m3 + 3 + 5m.
The standard form of the polynomial is m3 + 5m + 3.
(ii) − 7y + y5 + 3y3 – \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2y4 − y2
The standard form of the polynomial is y5+ 2y4+ 3y3− y2− 7y – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 1.7. Write the following polynomials in coefficient form.
(i) x3 − 2
x3 – 2 = x3 + 0x2 + 0x − 2
The coefficient form of the polynomial is (1, 0, 0, −2).
(ii) 5y
5y = 5y + 0
The coefficient form of the polynomial is (5, 0).
(iii) 2m4 − 3m2 + 7
2m4 − 3m2 + 7 = = 2m4 + 0m3 − 3m2 + 0m + 7
The coefficient form of the polynomial is (2, 0,−3, 0,7).
(iv) \(-\frac{2}{3}\)
The coefficient form of the polynomial \(-\frac{2}{3}\) is \((-\frac{2}{3})\)
Question 1.8. Write the polynomials in index form.
(i) (1, 2, 3)
(1, 2, 3) Here, the number of coefficients = 3.
∴ the degree of the polynomial is 3 − 1 = 2.
∴ The standard form is x2 + 2x + 3.
(ii) (5, 0, 0, 0, − 1)
(5, 0, 0, 0, − 1) Here, the number of coefficients = 5.
∴ the degree of the polynomial is 5 − 1 = 4.
∴ The standard form is 5x4 − 1.
(iii) (− 2, 2, − 2, 2)
(− 2, 2, − 2, 2) Here, the number of coefficients = 4.
∴ the degree of the polynomial is 4 − 1 = 3.
∴ The standard form is − 2x3 + 2x2 − 2x + 2.
Question 1.9. Write the appropriate polynomials in the boxes.
Quadratic polynomial : 3x2 + 5x; x2; 2x2 + 5x + 10
Cubic polynomial : x3 + x2 +x +5; x3 + 9
Linear polynomial : x + 7
Binomial : x + 7; 3x2 + 5x; x3 + 9
Trinomial : 2x2 + 5x + 10
Monomial : x2
Practice set 3.2
Question 2.1. Use the given letters to write the answer.
(i) There are ‘a’ trees in the village Lat. If the number of trees increases every year by ‘b’, then how many trees will there be after ‘x’ years?
The number of trees at present = a.
The number of trees increases by b in a year.
∴ the number of trees will increase by bx in x years
∴ the number of trees in the village Lat after x years will be a + bx.
Answer is : There will be a + bx trees in the village Lat.
(ii) For the parade there are y students in each row and x such row are formed. Then, how many students are there for the parade in all ?
The number of rows for parade = x
The number of students in each row = y.
∴ the total number of students for parade = x × y = xy
Answer is : The number of students present for the parade is xy.
(iii) The tens and units place of a two digit number is m and n respectively. Write the polynomial which represents the two digit number.
The place value of the digit m at tens place = m × 10 = 10m
The place value of the digit n at the units place = n × 1 = n.
∴ the number formed is 10m + n.
Answer is : The required number is 10m + n.
Question 2.2. Add the given polynomials.
(i) x3 − 2x2 − 9 ; 5x3 + 2x + 9
(x3 − 2x2 − 9) + (5x3 + 2x + 9)
= x3 − 2x2 − 9 + 5x3 + 2x + 9 ... (Removing brackets)
= x3 + 5x3 − 2x2 + 2x – 9 + 9 ... (Collecting like terms)
= 6x3 − 2x2 + 2x. ... (Adding like terms)
Answer is : 6x3 − 2x2 + 2x
(ii) − 7m4 + 5m3 + \(\sqrt{2}\) ; 5m4 − 3m3 + 2m2 + 3m − 6
(− 7m4 + 5m3 + \(\sqrt{2}\)) + (5m4 − 3m3 + 2m2 + 3m – 6)
= − 7m4 + 5m3 + \(\sqrt{2}\) + 5m4 − 3m3 + 2m2 + 3m – 6
= − 7m4 + 5m4 + 5m3 − 3m3 + 2m2 + 3m + \(\sqrt{2}\) – 6 ... (Collecting like terms)
= − 2m4 + 2m3 + 2m2 + 3m + \(\sqrt{2}\) – 6
Answer is : − 2m4 + 2m3 + 2m2 + 3m + \(\sqrt{2}\) – 6
(iii) 2y2 + 7y + 5 ; 3y + 9 ; 3y2 − 4y − 3
(2y2 + 7y + 5) + (3y + 9) + (3y2 − 4y – 3)
= 2y2 + 7y + 5 + 3y + 9 + 3y2 − 4y – 3
= 2y2 + 3y2 + 7y + 3y − 4y + 5 + 9 − 3
= 5y2 + 6y + 11
Answer is : 5y2 + 6y + 11
Question 2.3. Subtract the second polynomial from the first.
(i) x2 − 9x + \(\sqrt{3}\) ; − 19x + \(\sqrt{3}\) + 7x2
(x2 − 9x + \(\sqrt{3}\)) – (− 19x + \(\sqrt{3}\) + 7x2)
= x2 − 9x + \(\sqrt{3}\) + 19x − \(\sqrt{3}\) − 7x2
= x2 − 7x2 − 9x + 19x + \(\sqrt{3}\) − \(\sqrt{3}\)
= − 6x2 + 10x
Answer is : − 6x2 + 10x
(ii) 2ab2 + 3a2b − 4ab ; 3ab − 8ab2 + 2a2b
(2ab2 + 3a2b − 4ab) − (3ab − 8ab2 + 2a2b)
= 2ab2 + 3a2b − 4ab − 3ab + 8ab2 − 2a2b
= 2ab2 + 8ab2 + 3a2b − 2a2b − 4ab − 3ab
= 10ab2 + a2b − 7ab
Answer is : 10ab2 + a2b − 7ab
Question 2.4. Multiply the given polynomials.
(i) 2x ; x2 − 2x −1
(2x) × (x2 − 2x −1)
= 2x3 – 4x2 – 2x
Answer is : 2x3 – 4x2 – 2x
(ii) x5 − 1 ; x3 + 2x2 + 2
(x5 – 1) × (x3 + 2x2 + 2)
= x5(x3 + 2x2 + 2) −1(x3 + 2x2 + 2)
= x8 + 2x7 + 2x5 − x3 − 2x2 − 2
Answer is : x8 + 2x7 + 2x5 − x3 − 2x2 − 2
(iii) 2y + 1; y2 − 2y3 + 3y
(2y + 1) × (y2 − 2y3 + 3y)
= 2y(y2 − 2y3 + 3y) + 1(y2 − 2y3 + 3y)
= 2y3 – 4y4 + 6y2 + y2 − 2y3 + 3y
= 2y3 − 2y3 – 4y4 + 6y2 + y2 + 3y
= – 4y4 + 7y2 + 3y
Answer is : – 4y4 + 7y2 + 3y
Question 2.5. Divide first polynomial by second polynomial and write the answer in the form ‘Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder’.
(i) x3 − 64; x − 4
x3 – 64 = x3 + 0x2 + 0x – 64 ... (Index form of the polynomial)
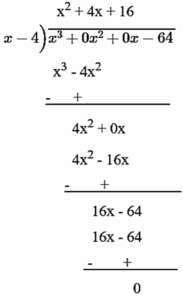
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
x3 – 64 = (x − 4) × (x2 + 4x + 16) + 0
(ii) 5x5 + 4x4 − 3x3 + 2x2 + 2; x2 − x
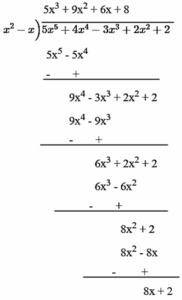
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
5x5 + 4x4 − 3x3 + 2x2 + 2 = (x2 – x) × (5x3 + 9x2 + 6x + 8) + 8x + 2
Question 2.6. Write down the information in the form of algebraic expression and simplify.
There is a rectangular farm with length (2a2 + 3b2) metre and breadth (a2 + b2) metre. The farmer used a square shaped plot of the farm to build a house. The side of the plot was (a2 − b2) metre. What is the area of the remaining part of the farm ?
Length of the rectangular farm = (2a2 + 3b2) m
Breadth of the rectangular farm = (a2 + b2) m
The total area of the farm = Length of the rectangular farm x Breadth of the rectangular farm
= (2a2 + 3b2) × (a2 + b2)
= 2a2 (a2 + b2) + 3b2 (a2 + b2)
= 2a4 + 2a2b2 + 3a2b2 + 3b4
= (2a4 + 5a2b2 + 3b2) sq. meter
Side of the square plot = (a2 − b2) meter.
Area of the square plot = (side) 2
= (a2 − b2) 2
= a4 − 2a2b2 + b4
Area of the remaining part of the farm = Total area of the farm − Area of the square plot
= (2a4 + 5a2b2 + 3b4) − (a4 − 2a2b2 + b4)
= 2a4 + 5a2b2 + 3b4 − a4 − 2a2b2 + b4
= 2a4 − a4 + 5a2b2 + 2a2b2 + 3b4 − b4
= a4 + 7a2b2 + 2b4
Answer is : The area of the remaining part of the farm is (a4 + 7a2b2 + 2b4) sq. meter.
Practice set 3.3
Question 3.1. Divide each of the following polynomials by synthetic division method and also by linear division method. Write the quotient and the remainder.
(i) (2m2 − 3m + 10) ÷ (m − 5)
Synthetic Division:
Dividend = 2m2 −3m + 10
Divisor = m – 5, Opposite of −5 = 5

The coefficient form of the quotient is (2, 7).
∴ Quotient = 2m + 7 and Remainder = 45
Linear Method:
2m2 −3m + 10
= 2m(m − 5) + 10m − 3m + 10
= 2m(m − 5) + 7(m − 5) + 35 + 10
= (m − 5) × (2m + 7) + 45
Answer is : The quotient is 2m + 7 and remainder is 45.
(ii) (x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5) ÷ (x + 2)
Synthetic division : The coefficient
form of the dividend x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5 is (1, 2, 3, 4, 5).
The divisor is x + 2. Opposite of 2 is − 2.
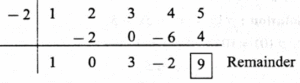
The coefficient form of the quotient is (1, 0, 3, −2).
∴ the quotient = x3 + 3x − 2.
Answer is : The quotient is x3 + 3x − 2 and the remainder is 9.
Linear Method :
x4 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) − 2x3 + 2x3 + 3x2 + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) – 6x + 4x + 5
= x3(x + 2) + 3x(x + 2) −2(x + 2) + 4 + 5
= (x + 2)(x3 + 3x − 2) + 9
Answer is : The quotient is x3 + 3x − 2 and remainder is 9.
(iii) (y3 − 216) ÷ (y − 6)
Synthetic division : First we write the index form of the dividend.
The index form is y3 + 0y2 + 0y − 216.
The coefficient form is (1, 0, 0, − 216)
The divisor is y − 6. Opposite of − 6 is 6.

The coefficient form of the quotient is (1, 6, 36).
∴ the quotient = y2 + 6y + 36.
Answer is : The quotient is y2 + 6y + 36 and the remainder is 0.
Linear Method :
y3 – 216 = y2(y − 6) + 6y2 − 216
= y2(y − 6) + 6y(y − 6) + 36y − 216
= y2(y − 6) + 6y(y − 6) + 36(y − 6) + 216 − 216
= (y − 6) (y2 + 6y + 36).
Answer is : The quotient is y2 + 6y + 36 and the remainder is 0.
(iv) (2x4 + 3x3 + 4x − 2x2 ) ÷ (x + 3)
Synthetic division : First we write the standard form of the dividend.
The standard form is 2x4 + 3x3 − 2x2 + 4x.
The index form is 2x4 + 3x3 − 2x2 + 4x + 0.
The coefficient form is (2, 3, − 2, 4, 0).
The divisor is x + 3. Opposite of 3 is − 3.
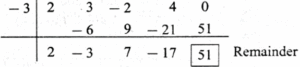
The coefficient form of the quotient is (2, −3, 7, − 17).
∴ the quotient = 2x3 − 3x2 + 7x − 17.
Answer is : The quotient is 2x3 − 3x2 + 7x – 17 and the remainder is 51.
Linear Method :
2x4 + 3x3 + 4x− 2x2
= 2x4 + 3x3 − 2x2 + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) − 6x3 + 3x3 − 2r2 + 4r
= 2x3(x + 3) − 3x2(x + 3) + 9x2 − 2x2 + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) − 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x + 3) − 21x + 4x
= 2x3(x + 3) − 3x2(x + 3) + 7x(x + 3) − 17(x + 3) + 51
= (x + 3)(2x3 − 3x2 + 7x − 17) + 51.
Answer is : The quotient is 2x3 − 3x2 + 7x – 17 and the remainder is 51.
(v) (x4 − 3x2 − 8) ÷ (x + 4)
Synthetic division : First we write the index form of the dividend.
The index form is x4 + 0x3 − 3x2 + 0x − 8.
The coefficient form is (1, 0, − 3, 0, − 8).
The divisor is x + 4. Opposite of 4 is − 4.
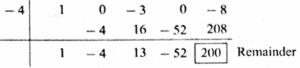
The coefficient form of the quotient is (1, −4, 13, − 52).
∴ the quotient = x3 − 4x2 + 13x − 52.
Answer is : The quotient is x3 − 4x2 + 13x − 52 and the remainder is 200.
Linear Method :
x4 − 3x2 − 8
= x3(x + 4) − 4x3 − 3x2 − 8
= x3(x + 4) − 4x2(x + 4) + 16x2 − 3x2 − 8
= x3(x + 4) − 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) − 52x − 8
= x3(x + 4) − 4x2(x + 4) + 13x(x + 4) − 52(x + 4) + 208 − 8
= (x + 4)(x3 − 4x2 + 13x − 52) + 200.
Answer is : The quotient is x3 − 4x2 + 13x − 52 and the remainder is 200.
(vi) (y3 − 3y2 + 5y − 1) ÷ (y − 1)
Synthetic division :
The coefficient form of the dividend y3 − 3y2 + 5y − 1 is (1, −3, 5, −1).
The divisor is y − 1. Opposite of − 1 is 1.
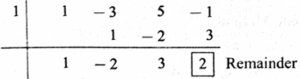
The coefficient form of the quotient is (1, −2, 3).
∴ the quotient = y2 − 2y + 3.
Answer is : The quotient is y2 − 2y + 3 and the remainder is 2.
Linear Method :
y3 − 3y2 + 5y − 1
= y2(y − 1) + y2− 3y2 + 5y − 1
= y2(y − 1) − 2y(y − 1) − 2y + 5y − 1
= y2(y − 1) − 2y(y − 1) + 3(y − 1) + 3 – 1
= y2(y − 1) − 2y(y − 1) + 3(y − 1) + 2
= (y − 1)(y2 − 2y + 3) + 2.
Answer is : The quotient is y2 − 2y + 3 and the remainder is 2.
Practice set 3.4
Question 4.1. For x = 0 find the value of the polynomial x2 − 5x + 5.
p (x) = x2 − 5x + 5
∴ p(0) = (0)2 − 5(0) + 5
= 0 – 0 + 5 = 5
p(0) = 5.
Question 4.2. If p(y) = y2 − 3\(\sqrt{2}\)y + 1 then find p (3\(\sqrt{2}\)) .
p (y) = y2 − 3\(\sqrt{2}\)y + 1
∴ p(3 ) = (3\(\sqrt{2}\))2 – 3\(\sqrt{2}\) x 3 + 1
= 9 × 2 – 9 × 2 + 1
= 18 – 18 + 1 = 1
p(3\(\sqrt{2}\)) = 1.
Question 4.3. If p(m) = m3 + 2m2 − m + 10 then p(a) + p(− a) = ?
p(m) = m3 + 2m2 − m + 10
∴ p(a) = a3 + 2a2 − a + 10 and
p(−a) = (−a)3 + 2(−a)2 − (−a) + 10
= −a3 + 2a2 + a + 10
∴ p(a) + p(−a)
= a3 + 2a2 − a + 10 − −a3 + 2a2 + a + 10
= 4a2 + 20
p(a) + p(−a) = 4a2 + 20.
Question 4.4. If p(y) = 2y3 − 6y2 − 5y + 7 then find p(2).
p(y) = 2y3 − 6y2 − 5y + 7
∴ p(2) = 2(2)3 − 6(2)2 − 5(2) + 7
=2 × 8 – 6 × 4 – 10 + 7
= 16 – 24 – 10 + 7
= − 11
p(2) = − 11.
Practice set 3.5
Question 5.1. Find the value of the polynomial 2x − 2x3 + 7 using given values for x.
(i) x = 3
p(x) = 2x − 2x3 +7
∴ p(3) = 2(3) − 2(3)3 + 7
= 6 – 2 × 27 + 7
= 6 – 54 + 7
= 13 − 54 = − 41
Answer is : The value of the given polynomial for x = 3 is − 41.
(ii) x = − 1
p(x) = 2x − 2x3 + 7
∴ p(−1) = 2x(−1) − 2(−1)3 + 7
= − 2 – 2 × (−1) + 7
= − 2 + 2 + 7 = 7
Answer is : The value of the given polynomial for x = −1 is 7.
(iii) x = 0
p(x) = 2x − 2x3 + 7
∴ p(0) = 2(0) − 2(0)3 + 7
= 0 − 2(0) + 7
= 0 – 0 + 7 = 7
Answer is : The value of the given polynomial for x = 0 is 7.
Question 5.2. For each of the following polynomial, find p(1), p(0) and p(− 2).
(i) p(x) = x3
| p(x) = x3
∴ p(1) = 13 = 1 p(1) = 1 |
p(x) = x3
∴ p(0) = 03 = 0 p(0) = 0 |
p(x) = x3
∴ p(−2) = (−2)3 = −8 p(−2) = −8 |
(ii) p(y) = y2 − 2y + 5
| p(y) = y2 − 2y + 5
∴ p(1) = 12 – 2 × 1 + 5 = 1 – 2 + 5 = 4 p(1) = 4 |
p(y) = y2 − 2y + 5
∴ p(0) = 02 – 2 × 0 + 5 = 0 – 0 + 5 = 5 p(0) = 5 |
p(y) = y2 − 2y + 5
∴ p(−2) = (−2)2 – 2 × (−2) + 5 = 4 + 4 + 5 = 13 p(−2) = 13 |
(iii) p(x) = x4 − 2x2 − x
| p(x) = x4 − 2x2 – x
∴ p(1) = 14 – 2(1)2 – 1 = 1 – 2 − 1 = −2 p(1) = −2 |
p(x) = x4 − 2x2 – x
∴ p(0) = 04 – 2(0)2 – 0 = 0 – 0 − 0 = 0 p(0) = 0 |
p(x) = x4 − 2x2 – x
∴ p(−2) = (−2)4 – 2(−2)2 – (−2) = 16 – 8 + 2 = 10 p(−2) = 10 |
Question 5.3. If the value of the polynomial m3 + 2m + a is 12 for m = 2, then find the value of a.
p (m) = m3 + 2m + a
∴ p(2) = (2)3 + 2(2) + a
∴ 12 = 8 + 4 + a ... [Given, p(2) = 12]
∴ 8 + 4 + a = 12
∴ a = 12 – 8 – 4 = 0
The value of a is 0.
Question 5.4. For the polynomial mx2 − 2x + 3 if p(− 1) = 7 then find m.
p(x) = mx2 − 2x + 3
∴ p(−1) = m(−1)2 − 2(−1) + 3 ... [Given, p (−1) = 7]
∴ 7 = m(1) + 2 + 3
∴ 7 = m + 5
∴ m = 7 – 5 = 2
Answer is : m = 2.
Question 5.5. Divide the first polynomial by the second polynomial and find the remainder using factor theorem.
(i) (x2 − 7x + 9) ; (x + 1)
p(x) = x2− 7x + 9 divisor = x + 1
∴ take x = − 1
p(−1) = (−1)2 − 7(−1) + 9
= 1 + 7 + 9 = 17
Answer is : The remainder is 17.
(ii) (2x3 − 2x2 + ax − a) ; (x − a)
p(x) = 2x3 − 2x2 + ax − a; divisor = x − a
∴ take x = a
p(a) = 2(a)3 − 2(a)2 + a(a) −a
= 2a3 − 2a2 + a2 – a
= 2a3 − a2 − a
Answer is : The remainder is 2a3 − a2 − a.
(iii) (54m3 + 18m2 − 27m + 5) ; (m − 3)
p(m) = 54m3 + 18m2 − 27m + 5; divisor = m − 3
∴ take m = 3
p(3) = 54(3)3 + 18(3)2 − 27(3) + 5
= 54(27) + 18(9) − 81 + 5
= 1458 + 162 – 81 + 5
=1625 − 81
= 1544
Answer is : The remainder is 1544.
Question 5.6. If the polynomial y3 − 5y2 + 7y + m is divided by y + 2 and the remainder is 50 then find the value of m.
p(y) = y3 − 5y2 + 7y + m; divisor = y + 2
∴ take y = − 2
p(−2) = (−2)3 − 5(−2)2 + 7(−2) + m
∴ 50 = − 8 − 5(4) − 14 + m ... (Given the remainder is 50)
∴ 50 = − 8 – 20 – 14 + m
∴ 50 = − 42 + m
∴ 50 + 42 = m
∴ m = 92
Answer is : The value of m is 92.
Question 5.7. Use factor theorem to determine whether x + 3 is factor of x2 + 2x − 3 or not.
By factor theorem, if x + 3 is a factor of the given polynomial, then p(−3) = 0.
p(x) = x2 + 2x − 3
∴ p(−3) = (−3)2 + 2(−3) − 3
= 9 – 6 − 3
∴ p(−3) = 0
Answer is : (x + 3) is the factor of x2 + 2x − 3.
Question 5.8. If (x − 2) is a factor of x3 − mx2 + 10x − 20 then find the value of m.
By factor theorem, if (x −2) is a factor of the given polynomial, then p(2) = 0.
p (x) = x3 − mx2 + 10x − 20
∴ p(2) = (2)3 − m(2)2 + 10(2) − 20
∴ 0 = 8 − 4m + 20 – 20
∴ 4m = 8
∴ m = 2
Answer is : The value of m is 2.
Question 5.9. By using factor theorem in the following examples, determine whether q(x) is a factor p(x) or not.
(i) p(x) = x3 − x2 − x − 1, q(x) = x − 1
By factor theorem, if q(x) is a factor of p(x), then p(x) = 0.
(i) p (x) = x3 − x2 − x − 1; divisor = q(x) = x − 1
∴ take x = 1.
p(1) = (1)3 − (1)2 – 1 − 1
= 1 – 1 – 1 – 1 = −2
∴ p(1) = − 2 ∴ p(1) ≠ 0
Answer is : q(x) = (x −1) is not a factor of p(x).
(ii) p(x) = 2x3 − x2 − 45, q(x) = x − 3
p(x) = 2x3 − x2 − 45 divisor = q(x) = x − 3
∴ take x = 3
p(3) = 2(3)3 − (3)2 − 45
= 2(27) – 9 − 45
= 54 – 54 = 0
Answer is : g(x) = x − 3 is a factor of p (x).
Question 5.10. If (x31 + 31) is divided by (x + 1) then find the remainder.
Dividend polynomial p(x) = x31 + 31; divisor = (x + 1)
∴ by remainder theorem, take x = − 1 …(Opposite of + 1)
p(x) = x31 + 31
∴ p(−1) = (−1)31 + 31
= − 1 + 31 = 30
∴ p(−1) = 30.
Answer is : The remainder is 30.
Question 5.11. Show that m − 1 is a factor of m21 − 1 and m22 − 1.
p(m) = m21 − 1; divisor = m − 1.
∴ by the factor theorem, take m = 1.
p(m) = m21 − 1
∴ p(1) = (1)21 – 1 = 1 – 1 = 0 ... (1)
p(m) = m22 − 1; divisor= m − 1
∴ take m = 1
p(m) = m22 − 1
∴ p(1) = 122 – 1 = 1 – 1 = 0 ... (1)
(m − 1) is a factor of m21 − 1 and m22 − 1. ∴ [From (1) and (2)]
Question 5.12. If x − 2 and x – \(\frac{1}{2}\) both are the factors of the polynomial nx2 − 5x + m, then show that m = n = 2
p (x) = nx2 − 5x + m; x − 2 is a factor of nx2 − 5x + m.
By factor theorem, p(2) = 0.
∴ p(2) = n(2)2 − 5(2) + m = 0
∴ 4n – 10 + m = 0 ... (1)
Also, x – \(\frac{1}{2}\) is a factor of nx2 − 5x + m.
By factor theorem, p\((\frac{1}{2})\) = 0
p\((\frac{1}{2})\) = n\((\frac{1}{2})^2\) − 5\((\frac{1}{2})\) + m = 0
\(\frac{n}{4}-\frac{5}{2}\) + m = 0
∴ n – 10 + 4m = 0 ... (Multiplying both the sides by 4) ... (2)
From (1) and (2),
4n – 10 + m = n – 10 + 4m
∴ 4n – n = 4m − m ∴ 3n = 3m
∴ n = m. ... (3)
Substituting n = m in equation (1),
4m – 10 + m = 0 ∴ 5m = 10 ∴ m = 2 ... (4)
From (3) and (4), m = n = 2.
Question 5.13.
(i) If p(x) = 2 + 5x then p(2) + p(− 2) − p(1).
p (x) = 2 + 5x
∴ p(2) = 2 + 5(2) = 2 + 10 = 12 ... (1)
p(−2) = 2 + 5(−2) = 2 − 10 = − 8 ... (2)
p(1) = 2 + 5(1) = 2 + 5 = 7 ... (3)
∴ p (2) + p(−2) − p (1) = 12 – 8 – 7 =− 3
Answer is : p(2) + p(−2) − p(1) = −3.
(ii) If p(x) = 2x2 − 5\(\sqrt{3}\)x + 5 then p(5\(\sqrt{3}\)).
p(x) = 2x2 − 5 x + 5.
p(5\(\sqrt{3}\)) = 2(5\(\sqrt{3}\))2− 5 (5\(\sqrt{3}\)) + 5
= 2(25 × 3) − (25 × 3) + 5
= 25 × 3 + 5
= 75 + 5 = 80
Answer is : p(5\(\sqrt{3}\)) = 80.
Practice set 3.6
Question 6.1. Find the factors of the polynomials given below.
(i) 2x2 + x − 1
2x2 + x − 1
= 2x2 + 2x – x − 1
= 2x(x + 1) −1(x + 1)
= (x + 1)(2x − 1)
Answer is : (x + 1)(2x − 1).
(ii) 2m2 + 5m − 3
2m2 + 5m − 3
= 2m2 + 6m – m − 3
= 2m(m + 3) − 1(m + 3)
= (m + 3)(2m − 1)
Answer is : (m + 3)(2m − 1).
(iii) 12x2 + 61x + 77
12x2 + 61x + 77
= 12x2 + 28x + 33x + 77 [12 × 77 = 4 × 3 × 11 × 7
= 4x(3x + 7) + 11(3x + 7) = 28 × 33 …(28 + 33 = 61)]
= (3x + 7)(4x + 11)
Answer is : (3x + 7)(4x + 11).
(iv) 3y2 − 2y − 1
= 3y2 − 3y + y − 1
= 3y(y − 1) + 1(y − 1)
= (y − 1)(3y + 1)
Answer is : (y − 1)(3y + 1).
(v) \(\sqrt{3}\)x2 + 4x + \(\sqrt{3}\)
\(\sqrt{3}\)x2 + 4x + \(\sqrt{3}\)
= \(\sqrt{3}\)x2 + 3x + 1x + \(\sqrt{3}\) [ \(\sqrt{3}\) x \(\sqrt{3}\) = 3, 3 × 1 = 3 ..(3 + 1 = 4)]
= \(\sqrt{3}\)x(x + \(\sqrt{3}\)) + 1(x + \(\sqrt{3}\))
= (x + \(\sqrt{3}\))( x + 1)
Answer is : (x + \(\sqrt{3}\) )( x + 1).
(vi) \(\frac{1}{2}\)x2 − 3x + 4
\(\frac{1}{2}\)x2 − 3x + 4
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x2 − 6x + 8)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x2 − 4x – 2x + 8)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)[x(x − 4) − 2(x − 4)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x − 4)(x − 2)
Answer is : \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x − 4)(x − 2)
Question 6.2. Factorize the following polynomials.
(i) (x2 − x)2 − 8 (x2 − x) + 12
(x2 − x)2 − 8(x2 − x) + 12
= m2 − 8m+ 12 ... [Substituting m for (x2 − x)]
= m2 − 2m − 6m + 12
= m(m − 2) − 6(m − 2)
= (m − 2)(m − 6)
= (x2 – x − 2)(x2 −x − 6) ... [Substituting (x2 − x) for m]
= (x2 − 2x + x − 2)(x2 − 3x + 2x − 6)
= [x(x − 2) + 1(x − 2)][x(x − 3) + 2(x − 3)]
= (x − 2)(x + 1)(x − 3)(x + 2)
Answer is : (x − 2)(x + 1)(x − 3)(x + 2).
(ii) (x − 5)2 − (5x − 25) − 24
(x − 5)2 − (5x − 25) – 24
= (x − 5)2 − 5(x − 5) − 24
= m2 − 5m − 24 ... [Substituting m for (x − 5)]
= m2 − 8m + 3m − 24
= m(m − 8) + 3(m − 8)
= (m − 8)(m + 3)
= (x − 5 − 8)(x − 5 + 3) ... [Substituting (x − 5) for m]
= (x − 13)(x − 2)
Answer is : (x − 13)(x − 2).
(iii) (x2 − 6x)2 − 8 (x2 − 6x +8) − 64
(x2 − 6x)2 − 8 (x2 − 6x +8) − 64 ... (Let x2 − 6x = m)
= m2 −8(m + 8) − 64
= m2 − 8m – 64 − 64
= m2 − 8m − 128
= m2 − 16m + 8m − 128
= m(m − 16) + 8(m − 16)
= (m − 16)(m + 8)
= (x2 − 6x − 16)(x2 − 6x + 8) ... [m = x2 − 6x]
= (x2 − 8x + 2x − 16)(x2 − 4x − 2x + 8)
= [x(x − 8) + 2(x − 8)][x(x − 4) − 2(x − 4)]
= [(x − 8)(x + 2)][(x − 4)(x − 2)]
= (x − 8)(x + 2)(x − 4)(x − 2)
Answer is : (x − 8)(x + 2)(x − 4)(x − 2).
(iv) (x2 − 2x + 3) (x2 − 2x + 5) − 35
(x2 − 2x + 3) (x2 − 2x + 5) – 35
= (m + 3)(m + 5) − 35 ... (Let x2 − 2x = m)
= m(m + 5) + 3(m + 5) − 35
= m2 + 5m + 3m + 15 − 35
= m2 + 8m − 20
= m2 + 10m − 2m − 20
= m(m + 10) − 2(m + 10)
= (m + 10)(m − 2)
= (x2 − 2x + 10)(x2 − 2x − 2) ... [m = x2 − 2x]
Answer is : (x2 − 2x + 10)(x2 − 2x − 2).
(v) (y + 2) (y − 3)(y + 8)(y + 3) + 56
(y + 2) (y − 3)(y + 8)(y + 3) + 56
= (y + 2)(y + 3)(y − 3)(y + 8) + 56
= [y(y + 3) + 2(y + 3)][y(y + 8) − 3(y + 8)] + 56
= (y2 + 3y + 2y + 6)(y2 + 8y − 3y − 24) + 56
= (y2 + 5y + 6)( y2 + 5y − 24) + 56
= (x + 6)(x − 24) + 56 ... (Let y2 + 5y = x)
= x(x − 24) + 6(x − 24) + 56
= x2 − 24x + 6x – 144 + 56
= x2 − 18x − 88
= x2 − 22x + 4x − 88
= x(x − 22) + 4(x − 22)
= (x − 22)(x + 4)
= (y2 + 5y − 22)(y2 + 5y + 4) ... [x = y2 + 5y]
= (y2 + 5y − 22)(y2 + 4y + y + 4)
= (y2 + 5y − 22)[y(y + 4) + 1(y + 4)]
= (y2 + 5y − 22)(y + 4)(y + 1)
Answer is : (y2 + 5y − 22)(y + 4)(y + 1).
(vi) (y2 + 5y)(y2 + 5y − 2) − 24
(y2 + 5y)(y2 + 5y − 2) – 24
=(n)(n − 2) − 24 ... (Let y2 + 5y = n)
= n2 − 2n − 24
= n2 − 6n + 4n − 24
= n(n − 6) + 4(n − 6) = (n − 6)(n + 4)
= (y2 + 5y − 6)(y2 + 5y + 4) ... [n = y2 + 5y]
= (y2 + 6y – y − 6)(y2 + 4y + y + 4)
= [y(y + 6) −1(y + 6)][y(y + 4) + 1(y + 4)]
= [(y + 6)(y − 1)][(y + 4)(y + 1)]
= (y + 6)(y − 1)(y + 4)(y + 1)
Answer is : (y + 6)(y − 1)(y + 4)(y + 1).
(vii) (x − 3)(x − 4)2(x − 5) – 6
(x − 3)(x − 4)2(x − 5) – 6
= [(x − 3)(x − 5)](x − 4)2 − 6
= [x(x − 5) − 3(x − 5)](x2 − 8x + 16) − 6
= [x2 − 5x − 3x + 15](x2 − 8x + 16) − 6
= (x2 − 8x + 15)(x2 − 8x + 16) − 6
= (m + 15)(m + 16) − 6 ... (Let x2 − 8x = m)
= m(m + 16) + 15(m + 16) − 6
= m2+ 16m + 15m + 240 − 6
= m2 + 31m + 234
= m2 + 18m + 13m + 234
= m(m + 18) + 13(m + 18)
= (m + 18)(m + 13)
= (x2 − 8x + 18)(x2 − 8x + 13) ... [m = x2 – 8x]
Answer is : (x2 − 8x + 18)(x2 − 8x + 13).
Problem set 3
Question 1. Write the correct alternative answer for each of the following questions.
(i) Which of the following is a polynomial ?
(A) \(\frac{x}{y}\) (B) − 3x (C) x−2 + 7 (D) \(\sqrt{2}\)x2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(D) \(\sqrt{2}\)x2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(In the other three, the powers of variables are not positive integers.)
(ii) What is the degree of the polynomial \(\sqrt{7}\) ?
(A) \(\frac{1}{2}\) (B) 5 (C) 2 (D) 0
(D) 0
(\(\sqrt{7}\) = \(\sqrt{7}\)x°. ∴ the degree is zero.)
(iii) What is the degree of the 0 polynomial ?
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) undefined (D) any real number
(C) undefined : [As per definition]
(iv) What is the degree of the polynomial 2x2 + 5x3 + 7 ?
(A) 3 (B) 2 (C) 5 (D) 7
(A) 3 : (The highest degree is 3.)
(v) What is the coefficient form of x3 − 1 ?
(A) (1, − 1) (B) (3, − 1) (C) (1, 0, 0, − 1) (D) (1, 3, − 1)
(C) (1, 0, 0, − 1)
[x3 – 1 = x3 + 0x2 + 0x −1 ... (Index form)
∴ coefficient form is (1, 0, 0, −1)]
(vi) p(x) = x2 − 7\(\sqrt{7}\)x + 3 then p(7\(\sqrt{7}\)) = ?
(A) 3 (B) 7\(\sqrt{7}\) (C) 42\(\sqrt{7}\) + 3 (D) 49\(\sqrt{7}\)
(A) 3
[x2 − 7\(\sqrt{7}\)x + 3
∴ p (7\(\sqrt{7}\)) = (7\(\sqrt{7}\))2 − 7 (7\(\sqrt{7}\)) + 3 = 49 × 7 – 49 × 7 + 3 = 3.]
(vii) When x = − 1, what is the value of the polynomial 2x3 + 2x ?
(A) 4 (B) 2 (C) − 2 (D) − 4
(D) – 4
(viii) If x − 1, what is a factor of the polynomial 3x2 + mx then find the value of m.
(A) 2 (B) − 2 (C) − 3 (D) 3
(C) − 3
[By remainder theorem,
3x2 + mx = 3(1)2 + m(1) = 3 + m = 0
∴ m = − 3]
(ix) Multiply (x2 − 3) (2x − 7x3 + 4) and write the degree of the product.
(A) 5 (B) 3 (C) 2 (D) 0
(A) 5
[(x2 − 3)(2x − 7x3 + 4) = x2 x x3 = x5
∴ degree of the product is 5]
(x) Which of the following is a linear polynomial ?
(A) x + 5 (B) x2 + 5 (C) x3 + 5 (D) x4 + 5
(A) x + 5
[(x + 5) is a linear polynomial with degree 1.]
Question 2. Write the degree of the polynomial for each of the following.
(i) 5 + 3x4 (ii) 7 (iii) ax7 + bx9 (a, b are constants.)
(i) The degree is 4
(ii) The degree is 0
(iii) The degree is 9.
Question 3. Write the following polynomials in standard form.
(i) 4x2 + 7x4 − x3 − x + 9
7x4 − x3 + 4x2 − x + 9
(ii) p + 2p3 + 10p2 + 5p4 − 8
5p4 + 2p3 + 10p2 + p − 8.
Question 4. Write the following polynomial in coefficient form.
(i) x4 + 16
(i) x4 + 16 = x4 + 0x3 + 0x2 + 0x + 16 ... (Index form)
∴ the coefficient form is (1, 0, 0, 0, 16).
(ii) m5 + 2m2 + 3m + 15
m5 + 2m2 + 3m + 15
= m5 + 0m4 + 0m3 + 2m2 + 3m + 15 ... (Index form)
∴ the coefficient form is (1, 0, 0, 2, 3, 15).
Question 5. Write the index form of the polynomial using variable x from its coefficient form.
(i) (3, −2, 0, 7, 18)
The number of coefficients = 5.
∴ the degree of the polynomial = 5 − 1 = 4.
The index form : 3x4 – 2x3 + 0x2 + 7x + 18.
(ii) (6, 1, 0, 7)
The number of coefficients = 4.
∴ the degree of the polynomial = 4 − 1 = 3.
The index form : 6x3 + x2 + 0x + 7.
(iii) (4, 5, −3, 0)
The number of coefficients = 4.
∴ the degree of the polynomial = 4 − 1 = 3.
The index form : 4x3 + 5x2 − 3x + 0.
Question 6. Add the following polynomials.
(i) 7x4 − 2x3 + x + 10 ; 3x4 + 15x3 + 9x2 − 8x + 2
(7x4 − 2x3 + x + 10) + (3x4 + 15x3 + 9x2 − 8x + 2)
= 7x4 − 2x3 + x + 10 + 3x4 + 15x3 + 9x2 − 8x + 2
= 7x4 + 3x4 − 2x3 + 15x3 + 9x2 + x − 8x + 10 + 2 ... (Collecting like terms)
= 10x4 + 13x3 + 9x2 − 7x +12
Answer is : 10x4 + 13x3 + 9x2 − 7x +12.
(ii) 3p3q + 2p2q + 7 ; 2p2q + 4pq − 2p3q
(3p3q + 2p2q + 7) + (2p2q + 4pq − 2p3q)
= 3p3q + 2p2q + 7 + 2p2q + 4pq − 2p3q
= 3p3q − 2p3q + 2p2q + 2p2q + 4pq + 7 ... (Collecting like terms)
= p3q + 4p2q + 4pq + 7.
Answer is : p3q + 4p2q + 4pq + 7.
Question 7. Subtract the second polynomial from the first.
(i) 5x2 − 2y + 9 ; 3x2 + 5y − 7
(5x2 − 2y + 9) − (3x2 + 5y − 7)
= 5x2 − 2y + 9 − 3x2 − 5y + 7
= 5x2 − 3x2 −2y − 5y + 9 + 7 ... (Collecting like terms)
= 2x2 − 7y + 16
Answer is : 2x2 − 7y + 16
(ii) 2x2 + 3x + 5 ; x2 − 2x + 3
(2x2 + 3x + 5) − (x2 − 2x + 3)
= 2x2 + 3x + 5 − x2 + 2x − 3
= 2x2 − x2 + 3x + 2x + 5 – 3 ... (Collecting like terms)
= x2 + 5x + 2.
Answer is : x2 + 5x + 2
Question 8. Multiply the following polynomials.
(i) (m3 − 2m + 3)(m4 − 2m2 + 3m + 2)
(m3 − 2m + 3)( m4 − 2m2 + 3m + 2)
= m3(m4 − 2m2 + 3m + 2) − 2m(m4 − 2m2 + 3m + 2) + 3(m4 − 2m2 + 3m + 2)
=m7 − 2m5 + 3m4 + 2m3 − 2m5 + 4m3 − 6m2 − 4m + 3m4 − 6m2 + 9m + 6
= m7 − 2m5 − 2m5 + 3m4 + 3m4 + 2m3 + 4m3 − 6m2 − 6m2 − 4m + 9m + 6
= m7 − 4m5 + 6m4 + 6m3 − 12m2 + 5m + 6
Answer is : m7 − 4m5 + 6m4 + 6m3 − 12m2 + 5m + 6.
(ii) (5m3 − 2)(m2 − m + 3)
(5m3 − 2)( m2 − m + 3)
= 5m3(m2 – m + 3) − 2(m2 – m + 3)
= 5m5 − 5m4 + 15m3 − 2m2 + 2m − 6
Answer is : 5m5 − 5m4 + 15m3 − 2m2 + 2m − 6.
Question 9. Divide polynomial 3x3 − 8x2 + x + 7 by x − 3 using synthetic method and write the quotient and remainder.
Dividend = 3x3 − 8x2 + x + 7
Its coefficient form : (3, −8. 1, 7)
Divisor = x – 3. Opposite of − 3 is 3.
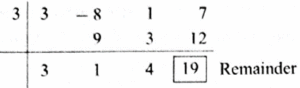
The coefficient form of quotient = (3, 1, 4)
Answer is : The quotient = 3x2 + x + 4; remainder = 19.
Question 10. For which the value of m, x + 3 is the factor of the polynomial x3 − 2mx + 21 ?
(x + 3) is a factor of
p (x) = x3 − 2mx + 21.
∴ by factor theorem, p (−3) = 0.
p (x) = x3 − 2mx + 21.
∴ p(−3) = (−3)3 − 2m(−3) + 21
∴ 0 = − 27 + 6m + 21
∴ 0 = − 6 + 6m ∴ 6 = 6m ∴ m = 1
Answer is : For the value of m = 1.
Question 11. At the end of the year 2016, the population of villages Kovad, Varud, Chikhali is 5x2 − 3y2, 7y2 + 2xy and 9x2 + 4xy respectively. At the beginning of the year 2017, x2 + xy − y2, 5xy and 3x2 + xy persons from each of the three villages respectively went to another village for education then what is the remaining total population of these three villages ?
Total population of the three villages
= (5x2 − 3y2) + (7y2 + 2xy) + (9x2 + 4xy)
= 5x2 − 3y2 + 7y2 + 2xy + 9x2 + 4xy
= 5x2 + 9x2 − 3y2 + 7y2 + 2xy + 4xy
= 14x2 + 4y2 + 6xy
Total number of persons who went to another village for education
= (x2 + xy − y2) + 5xy + (3x2 + xy)
= x2 + xy − y2 + 5xy + 3x2 + xy
= x2 + 3x2 − y2 + xy + 5xy + xy
= 4x2 − y2 + 7xy
∴ Remaining total population of the three villages = Total population of the three villages − Total number of persons who went to another village for education
= (14x2 + 4y2 + 6xy) − (4x2 − y2 + 7xy)
= 14x2 + 4y2 + 6xy − 4x2 + y2 − 7xy
= 14x2 − 4x2 + 4y2 + y2 + 6xy − 7xy
= 10x2 + 5y2 − xy
Answer is : The remaining total population of these three villages is 10x2 + 5y2 – xy.
Question 12. Polynomials bx2 + x + 5 and bx3 − 2x + 5 are divided by polynomial x − 3 and the remainders are m and n respectively. If m − n = 0 then find the value of b.
Let p(x) = bx2 + x + 5 and q(x) = bx3 − 2x + 5.
The remainder when p(x) = bx2 + x + 5 is divided by (x − 3) is m.
By remainder theorem,
Remainder = p(3) = m
∴ b(3)2 + 3 + 5 = m
∴ m = 9b + 8 ... (1)
The remainder when q(x) = bx3 − 2x + 5 is divided by (x − 3) is n.
By remainder theorem,
Remainder= q(3) = n
∴ b(3)3 −2(3) + 5 = n
∴ n = 27b – 6 + 5 = 27b – 1 ... (2)
Now,
m – n = 0
(9b + 8) − (27b − 1) = 0 ….[Using (1) and (2)]
9b − 27b + 8 + 1 = 0
= − 18b + 9 = 0
− 18b = − 9
b = \(\frac{-9}{-18}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer is : The value of b is \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 13. Simplify. (8m2 + 3m − 6) − (9m − 7) + (3m2 − 2m + 4)
(8m2 + 3m − 6) − (9m − 7) + (3m2 − 2m + 4)
= 8m2 + 3m – 6 − 9m + 7 + 3m2 − 2m + 4
= 8m2 + 3m2 + 3m − 9m − 2m – 6 + 7 + 4
= 11m2 − 8m + 5
Answer is : 11m2 − 8m + 5
Question 14. Which polynomial is to be subtracted from x2 + 13x + 7 to get the polynomial 3x2 + 5x − 4?
Let p(x) be the polynomial which is to be subtracted from x2 + 13x + 7 to get the polynomial 3x2 + 5x − 4.
∴ (x2 + 13x + 7) − p(x) = 3x2 + 5x − 4
p(x) = (x2 + 13x + 7) − (3x2 + 5x − 4)
p(x) = x2 + 13x + 7 − 3x2 − 5x + 4
p(x) = x2 − 3x2 + 13x − 5x + 7 + 4
= p(x) = − 2x2 + 8x + 11
Answer is : The required polynomial is −2x2 + 8x + 11.
Question 15. Which polynomial is to be added to 4m + 2n + 3 to get the polynomial 6m + 3n + 10?
The required polynomial can be obtained by subtracting the polynomial 4m + 2n + 3 from 6m + 3n + 10.
∴ Required polynomial
∴ (4m + 2n + 3) + p(a) = (6m + 3n + 10)
∴ p(a) = (6m + 3n + 10) − (4m + 2n + 3)
= 6m + 3n + 10 − 4m − 2n − 3
= 6m − 4m + 3n − 2n + 10 − 3
= 2m + n + 7
Thus, the polynomial 2m + n + 7 is to be added to 4m + 2n + 3 to get the polynomial 6m + 3n + 10.
Click on link to get PDF from store :
PDF : Class 9th-Mathematics-1-Chapter-3-Polynomials- Notes
PDF : Class 9th-Mathematics-1-Chapter-3-Polynomials- Solution
All Chapter Notes-Class-9-Mathematics-1 and 2-(16-PDF)-Rs.68
All Chapter's Solution-Class-9-Mathematics-1 and 2-(16-PDF)-Rs.90
All Chapter's Notes+Solutions-Class-9-Mathematics-1 and 2-(32-PDF)-Rs.140
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 9th-Mathematics – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-2-Real Numbers – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-4-Ratio and Proportion – Online Solutions
