Co-ordinate Geometry
Class-9-Mathematics-2-Chapter-7-Maharashtra Board
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Axis, Origin, Quadrant :
- The location of a point can be fully described using its distance from two mutually perpendicular lines.
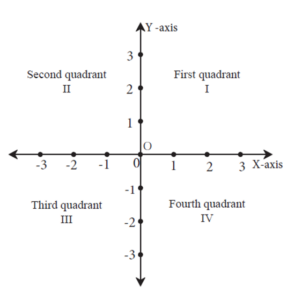
- To locate a point in a plane, a horizontal number line is drawn in the plane. This number line is called the X-axis.
- Another number line intersecting the X-axis at the point marked O and perpendicular to the X-axis is drawn. This number line is called the Y-axis.
- The number 0 (Zero) is represented by the same point on both the number lines. This point is called the origin and is shown by the letter O.
- On the X-axis, the positive numbers are shown on the right of O and the negative numbers on the left.
- On the Y-axis, the positive numbers are shown above O and the negative numbers below it.
- The X and Y-axes divide the plane into four parts, each of which is called a quadrant. The quadrants are numbered I, II, III and IV in the anticlockwise direction.
The coordinates of a point in a plane :
The point P is shown in the plane determined by the X-axis and the Y-axis.
Its position can be determined by its distance from the two axes.
Draw seg PM ⊥ X-axis and seg PN ⊥ Y-axis.
The coordinate of point M on X-axis is 2 and the coordinate of point N on Y-axis is 3.
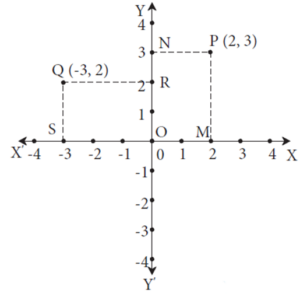
∴ the x-coordinate of point P is 2 and its y-coordinate is 3.
According to the convention, x-coordinate is mentioned first.
∴ the coordinates of point P are (2, 3).
Similarly, the coordinate of point Q are ( - 3, 2).
The coordinates of points on the axes :
(i) The x-coordinate of point M is its distance from the Y-axis.
The distance of point M from the Y-axis is 3. The distance of the point M from the X-axis is zero.
∴ the y-coordinate of point M is 0. Thus, the coordinates of point A on the X-axis are (3, 0).
(ii) The y-coordinate of point N on the Y-axis is 4, because it is at a distance of 4 from the X-axis. Its distance from Y-axis is zero.
∴ the coordinates of point N on the Y-axis are (0, 4).
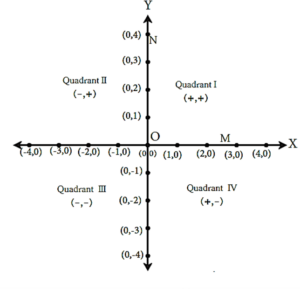
The origin O is on both the axes. Hence, its distance from X-axis and Y-axis is zero.
∴ the coordinates of O are (0, 0).
Remember :
- The y-coordinate of every point on the X-axis is zero.
- The x-coordinate of every point on the Y-axis is zero.
- The coordinates of origin are (0, 0).
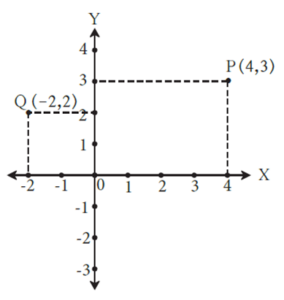
To plot the points with given coordinates :
Suppose we have to plot the points P (4,3) and Q (-2,2)
Steps for plotting the points
(i) Draw X-axis and Y-axis on the plane. Show the origin.
(ii) To find the point P (4,3), draw a line parallel to the Y-axis through the point on X axis which represents the number 4.
Through the point on Y-axis which represents the number 3 draw a line parallel to the X-axis .
(iii) The point of intersection of these two lines parallel to the Y and X-axis respectively, is the point P (4,3).
(iv) In the same way, plot the point Q (-2, 2) .
Lines parallel to the X-axis :
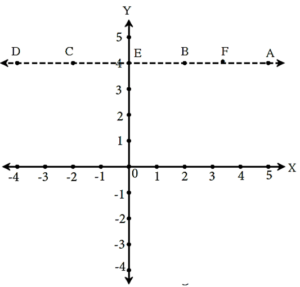
- In the figure, points A, B, C, D, E, F on line AD have the same y-coordinates.
- All the points are collinear.
- Line AD is parallel to the X-axis.
- The y-coordinate of every point on line AD is 4.
- The equation of the line parallel to the X-axis and 4 units above it is y = 4.
Remember :
- If b > 0 and we draw the line y = b through the point (0, b), it will be above the X-axis and parallel to it.
- If b < 0, then the line y = b will be below X-axis and parallel to it.
- The equation of a line parallel to the X-axis is in the form y = b.
Line parallel to the Y-axis :
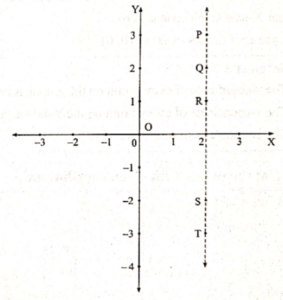
- In the figure, points P, Q, R, S, T on line PT have the same .x-coordinates.
- This line is parallel to the Y-axis.
- The x-coordinate of every point on line PT is 2.
- The equation of a line parallel to the Y-axis and on the right of it is x = 2.
Remember :
If we draw the line x = a parallel to the Y-axis and passing through the point (a, 0) and if a > 0, then the line will be to the right of the Y-axis.
If a < 0, then the line will be to the left of the Y-axis.
The equation of a line parallel to the Y-axis is in the form x = a.
(i) The y-coordinate of every point on the X-axis is zero. Conversely, every point whose y-coordinate is zero is on the X-axis. ∴ the equation of the X-axis is y = 0.
(ii) The x-coordinate of every point on the Y-axis is zero. Conversely, every point whose x-coordinate is zero is on the Y-axis. ∴ the equation of the Y-axis is x = 0.
Graph of a linear equations :
Example : Draw the graph of x = 2 and y = - 3.
Solution :
- On the graph paper draw the X-axis and Y-axis.
- Given : x = 2. Draw a line on the right of Y-axis at a distance of 2 units from it and parallel to it.
- Given : y = - 3. Draw a line below the X-axis at a distance of 3 units from it and parallel to it.
- These lines, parallel to the two axes, are the graphs of the given equations.
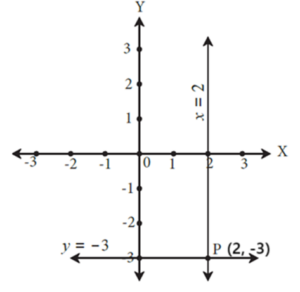
- Write the coordinate of the point P, the point of intersection of these two lines.
- The coordinates of P are (2, - 3).
The graph of a linear equation in the general form :
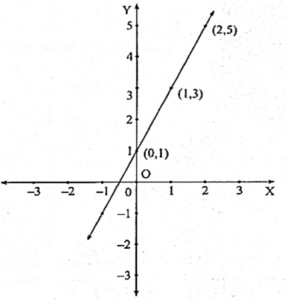
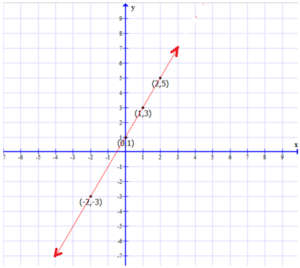
Example 1 : On a graph paper, plot the points (0,1) (1,3) (2,5). Are they collinear ? If so, draw the line that passes through them.
Answer :
Since the points lie on the same straight line. Therefore, the points (0,1), (1,3), and (2,5) are collinear.
From the Graph :
- The line passes through quadrants I, II and III.
- The coordinates of the point at which it intersects the Y-axis is (0,1)
- The coordinates of the one point which is in the third quadrant which lies on this line is (-1, -1).
Example 2 : 2x - y + 1 = 0 is a linear equation in two variables in general form. Let us draw the graph of this equation.
The graph of a linear equation in general form is a line.
2x -y +1 = 0 is a linear equation in two variables in general form.
To draw the graph of this equation, choose at least three convenient values of x and find the corresponding values of y.
For example, If x = 0, then substituting this value of x in the equation we get y = 1.
Similarly, find the values of y when x = 1, 2, -2.
Write these values in tabular form.
Plot the ordered pairs (x, y) from the table on a graph paper, choosing suitable scale.
Join these points by a straight line.
2x - y = -1 :
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | -2 |
| y | 1 | 3 | 5 | -3 |
| (x, y) | (0, 1) | (1, 3) | (2, 5) | (-2, -3) |
Click on link to get PDF from store :
PDF : Class 9th-Mathematics-2-Chapter-7-Co-ordinate Geometry-Notes
PDF : Class 9th-Mathematics-2-Chapter-7-Co-ordinate Geometry-Solution
All Chapter Notes-Class-9-Mathematics-1 and 2-(16-PDF)-Rs.68
All Chapter's Solution-Class-9-Mathematics-1 and 2-(16-PDF)-Rs.90
All Chapter's Notes+Solutions-Class-9-Mathematics-1 and 2-(32-PDF)-Rs.140
Main Page : – Maharashtra Board Class 9th-Mathematics – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Mathematics-2-Chapter-6-Circle – Online Notes
Next Chapter : Mathematics-2-Chapter-8-Trigonometry – Online Notes
