Human Eye and Colourful World
NCERT--CBSE-Class-10-Science-Chapter-10
Solutions
In−text Solutions (Page 164)
Question 1. What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
The power of accommodation of the eye is the maximum variation of its power for focusing on near and far (distant) objects.
For a normal eye, the power of accommodation is about four dioptres.
Question 2. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
The person is suffering from myopia or short sightedness.
To correct this defect of vision, concave lens of suitable focal length is used.
Question 3. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
For a human eye with normal vision, the far point is at infinity and near point is at 25 cm from the eye.
Question 4. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
The child is suffering from myopia. He should use concave lenses of suitable focal length.
Exercise Solutions
Question 1. The human eye can focus on objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) presbyopia.
(b) accommodation.
(c) near-sightedness.
(d) far-sightedness.
(b) accommodation.
Explanation : Accommodation is the ability of eye lens to focus both near and distant objects by adjusting its focal length.
Question 2. The human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) cornea.
(b) iris.
(c) pupil.
(d) retina.
(d) retina.
Explanation : Retina is the light sensitive surface of eye which acts like screen on which the image is formed.
Question 3. The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
(a) 25 m.
(b) 2.5 cm.
(c) 25 cm.
(d) 2.5 m.
(c) 25 cm
Explanation : The minimum distance at which an object can be seen most distinctly without any strain is 25 cm.
Question 4. The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) pupil.
(b) retina.
(c) ciliary muscles.
(d) iris.
(c) ciliary muscles
Ciliary muscles contract and expand in order to change the lens shape for focussing image at retina.
Question 5. A person needs a lens of power –5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
(i) We know that,
Focal length = \(\frac{1}{Power}=\frac{1}{-5.5}\) = -0.18 m …[given, power, P = - 5.5 D]
f = -0.18 m
f = -18 cm
(i)
Focal length = \(\frac{1}{Power}=\frac{1}{+1.5}\) = 0.67 m …[given, power, P = +1.5 D]
f = 0.67 m
f = 67 cm
Question 6. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
The remedial lens should make the objects at infinity appear at the far point.
∴ For object at infinity, u = -∞
Far point distance of the defected eye, v = -80 cm
By lens formula, \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\) = \(\frac{1}{-80}-\frac{1}{-∞}\) = \(-\frac{1}{80}\) + 0
∴ f = - 80 cm
Power, P = \(\frac{100}{f(in\,cm)} = \frac{100}{-80}\) = -1.25 D.
Negative sign shows that the remedial lens is a concave lens.
Question 7. Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Hypermetropia can be corrected by using convex lens.
The ray diagram is as follows:
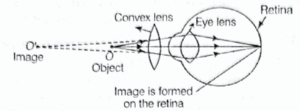
Given : Image distance, v = -1m = -100 cm, Object distance, u = -25 cm
[For correction, image should be at 1m]
From lens formula, \(\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\)
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{u-v}{uv}\)
∴ f = \(\frac{uv}{u-v}\) = \(\frac{-25×(-100)}{(-25)-(-100)}\) = \(\frac{2500}{75}\) = \(\frac{100}{3}\) cm = \(\frac{1}{3}\) m
Power of lense, P = \(\frac{1}{f(in\,m)}=\frac{1}{1/3}\) = +3D
Question 8. Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
As our eye cannot focus the objects placed closer than 25 cm on the retina, we are unable to see the objects clearly.
Question 9. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
The image distance remains the same because the focal length of the eye lens gradually changes to maintain the position of image on the retina of the eye.
Question 10. Why do stars twinkle?
- Stars twinkle due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight passes through different layers of atmospheric medium of gradually changing refractive index. So, it is refracted multiple times.
- As the apparent position of star and the physical condition of the earth's atmosphere are not constant. The amount of starlight entering the eye flickers and gives a twinkling effect.
Question 11. Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
Planets are very close to the earth as compared to the stars. They also act as extended sources of light. The total variation in the amount of light entering our eyes from all the individual point sized sources will average out to zero, which nullify the twinkling effect of each other. So, planets do not twinkle.
Question 12. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Sky appears dark to the astronauts because there is no atmosphere and hence no scattering of light takes place in the space.
Click on below links to get PDF from store
PDF : Class 10th-Science-Chapter-10-Human Eye and Colourful World-Notes
PDF : Class 10th-Science-Chapter-10-Human Eye and Colourful World-Solution
Main Page : NCERT-Class-10-Science – All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 9 : Light – Reflection and Refraction – Online Solutions
Next Chapter : Chapter-11-Electricity – Online Solutions
